Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence
electron(s) between atoms. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two
oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to
become a positively charged cation, whereas the nonmetal accepts those
electrons to become a negatively charged anion. Ionic bonds require an
electron donor, often a metal, and an electron acceptor, a nonmetal.
Ionic bonding is observed because metals(
elements in left hand side of periodic table) have few electrons in
their outer-most orbitals. By losing those electrons, these metals can
achieve noble gas configuration and satisfy the octet rule. Similarly,
nonmetals( elements in right hand side of periodic table) that have close to 8
electrons in their valence shells tend to readily accept electrons to achieve
noble gas configuration. In ionic bonding, more than 1 electron can be donated
or received to satisfy the octet rule. The charges on the anion and cation
correspond to the number of electrons donated or received. In ionic bonds, the
net charge of the compound must be zero.
This sodium molecule donates the lone electron in
its valence orbital in order to achieve octet configuration. This creates a
positively charged cation due to the loss of electron.
Ionic bonds are endothermic ,means bond requires energy , it
takes from surroundings ,so ionic bonds are unfavorable , but ionic are not unfavorable they are favorable,
this is possible by electrostatic attraction of forces (coulombs law :the magnitude of the electrostatic force of interaction
between two point charge is directly proportional to the scalar
multiplication of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the
square of the distance between them.)
(Ionization energy
,minimum energy required for the removing of electron from atom, metal has positive ionization energy and
electron affinity ,energy release by the new bond formation, non metals is also positive electron affinity
that why ionic bond shows is
endothermic.)
Examples of ionic bonds and ionic compounds:
NaBr - sodium bromide
KBr - potassium bromide
NaCl - sodium chloride
NaF - sodium fluoride
KI - potassium iodide
KCl - potassium chloride
CaCl2 - calcium chloride
K2O - potassium oxide
MgO - magnesium oxide
NaCl - sodium chloride
Sodium (2,8,1) has 1 electron more than a stable noble gas structure (2,8). It's ready to give one electron and would become more stable.
Chlorine (2,8,7) has 1 electron short of a stable noble gas structure (2,8,8). It's ready gain an electron and would become more stable.
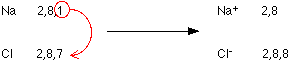
NaBr and NaF is also same process .
MgO:
Examples of ionic bonds and ionic compounds:
NaBr - sodium bromide
KBr - potassium bromide
NaCl - sodium chloride
NaF - sodium fluoride
KI - potassium iodide
KCl - potassium chloride
CaCl2 - calcium chloride
K2O - potassium oxide
MgO - magnesium oxide
NaCl - sodium chloride
Sodium (2,8,1) has 1 electron more than a stable noble gas structure (2,8). It's ready to give one electron and would become more stable.
Chlorine (2,8,7) has 1 electron short of a stable noble gas structure (2,8,8). It's ready gain an electron and would become more stable.
NaBr and NaF is also same process .
MgO:
Magnesium oxide is more strong ionic bond when compared to NaCl
Magnesium(2,8,2)
:it has two electrons more to achieve noble gas structure (2,8),it is
ready to give 2 electrons and would become more stable .
Oxygen (2, 4), has 2 electron short of a stable noble gas structure
(2,8). It's ready gain 2 electron and would
become more stable.
CaCl2 - calcium chloride:
Calcium:(2,8,8,2):it
has two electrons more to achieve noble gas structure (2,8),it is ready
to give 2 electrons and would become more stable. Chloride requires
only one atom so calcium gives electrons to two chloride atoms to form
ionic bond.